Rotating Shapes
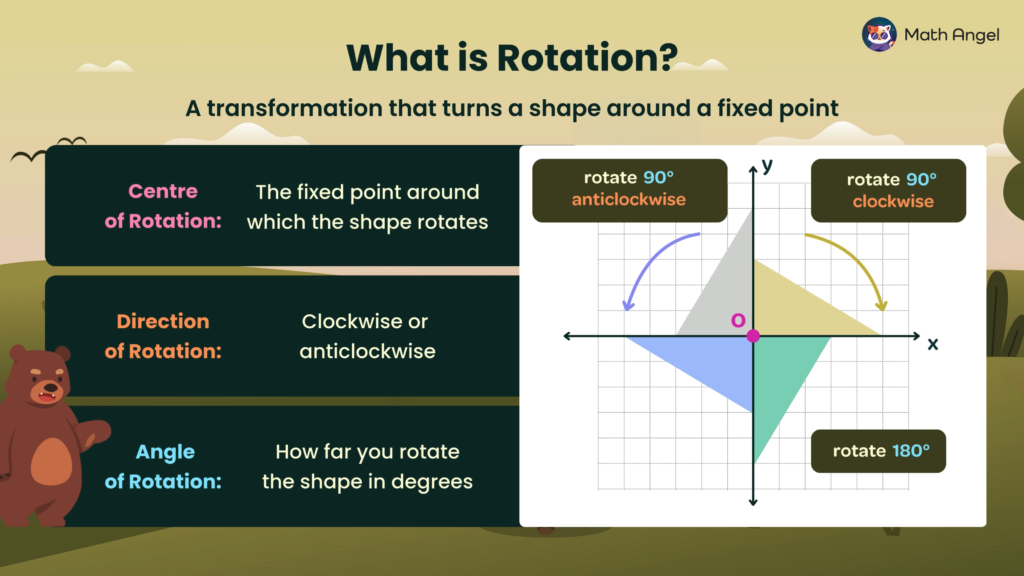
Open to access this content
Translating Shapes
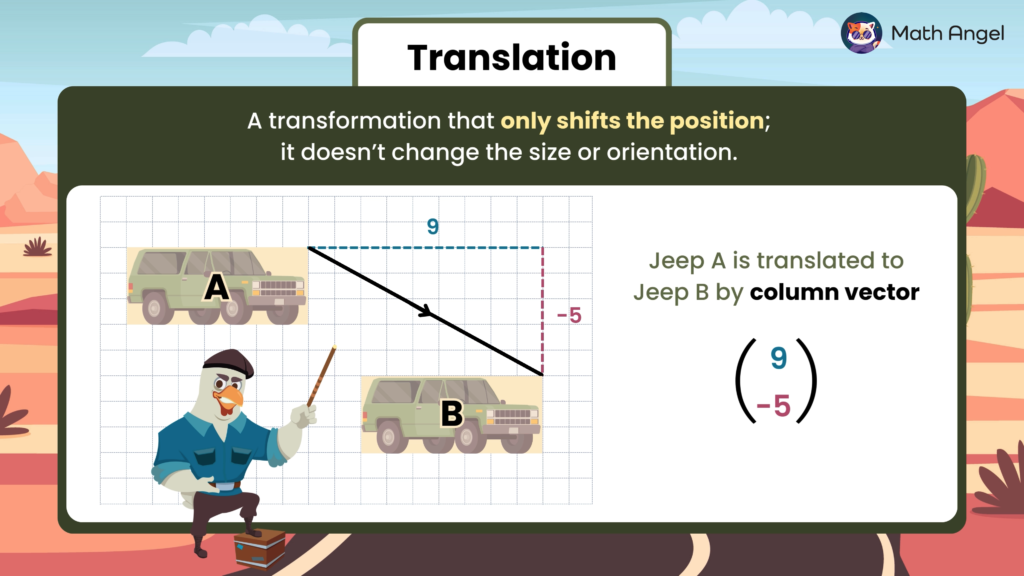
Open to access this content
Area of a Triangle
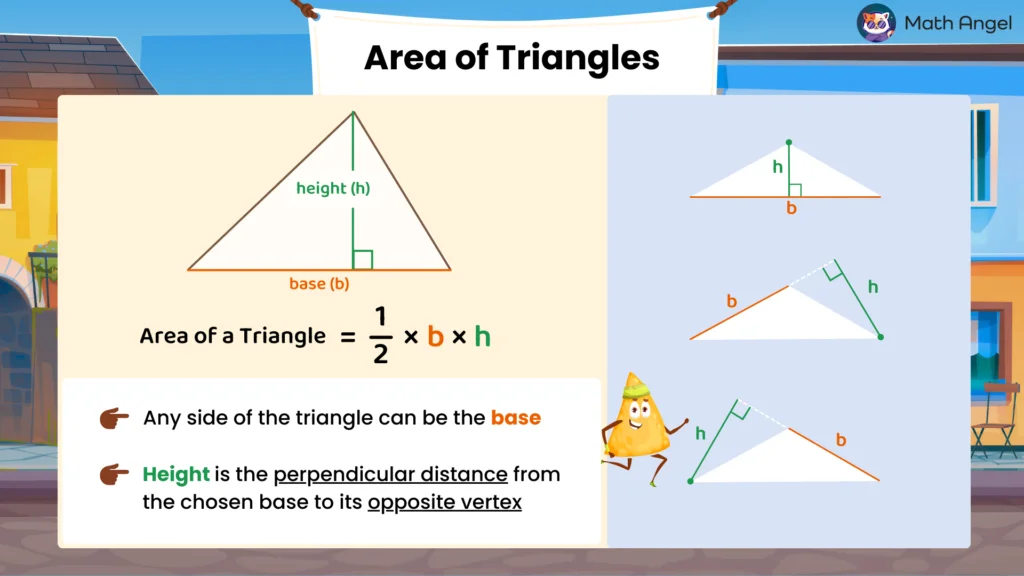
Open to access this content
Area of Compound Shapes
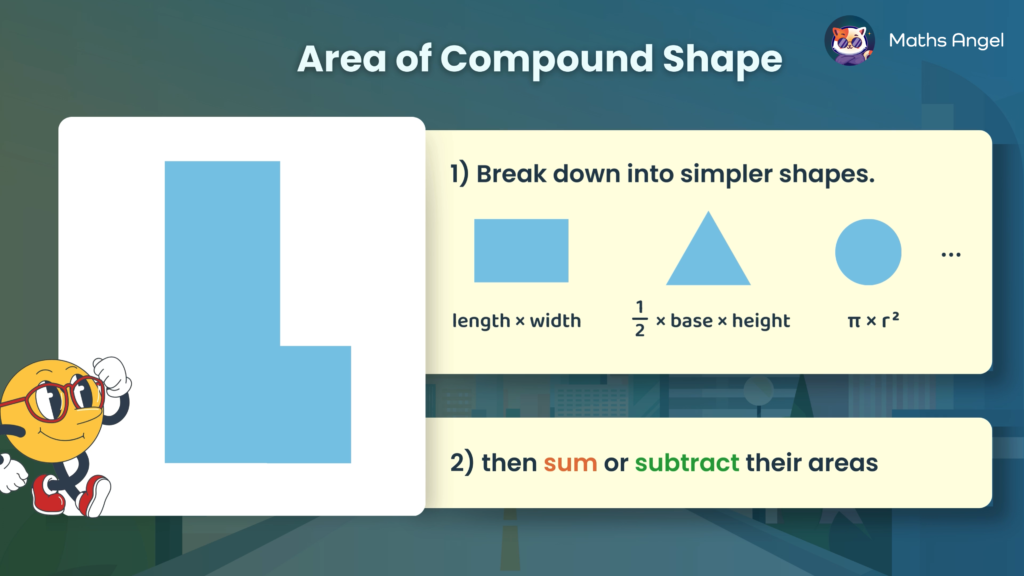
Open to access this content
Rotational Symmetry
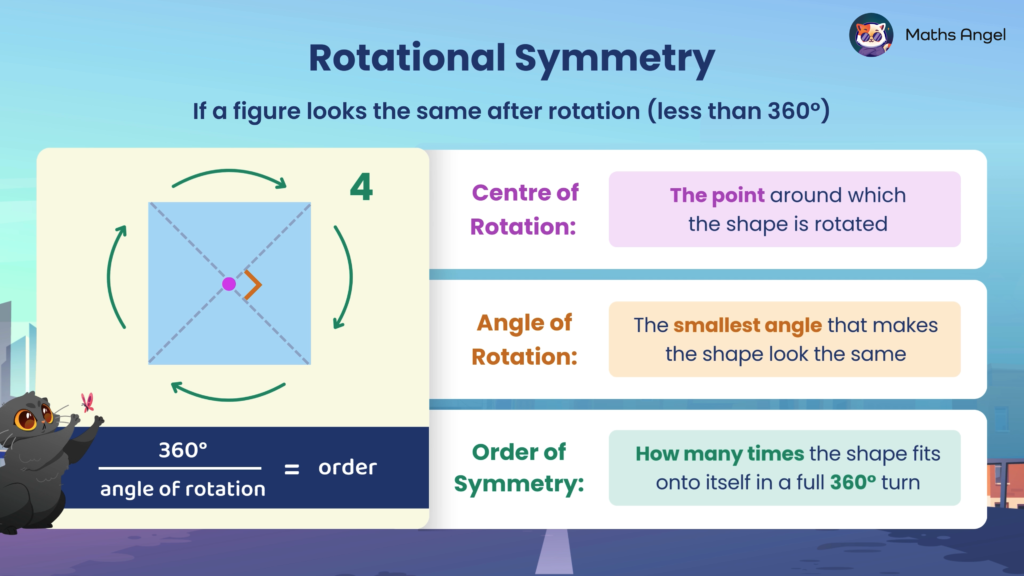
Open to access this content
Line of Symmetry and Reflection Symmetry
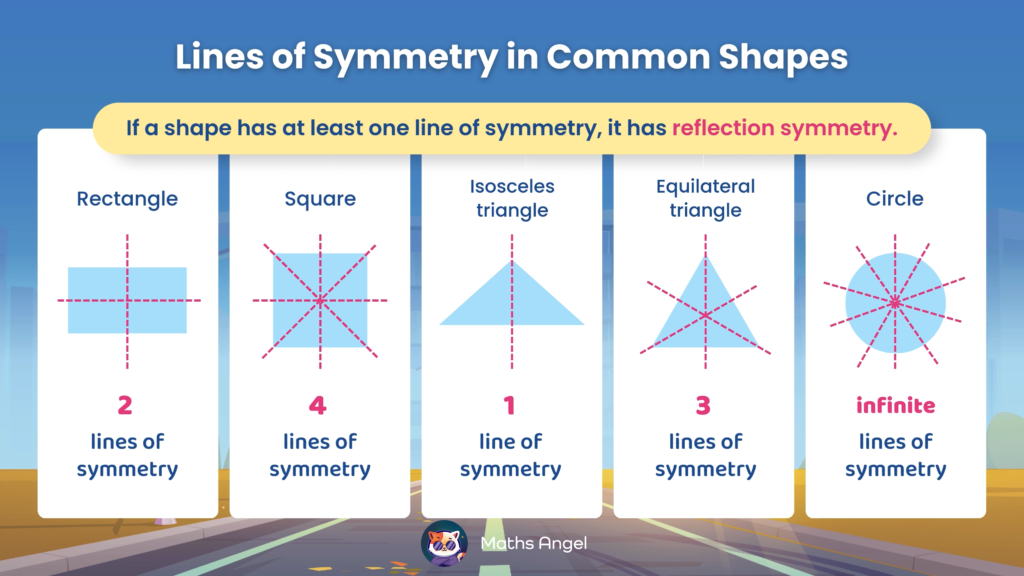
Open to access this content
Pythagoras Theorem
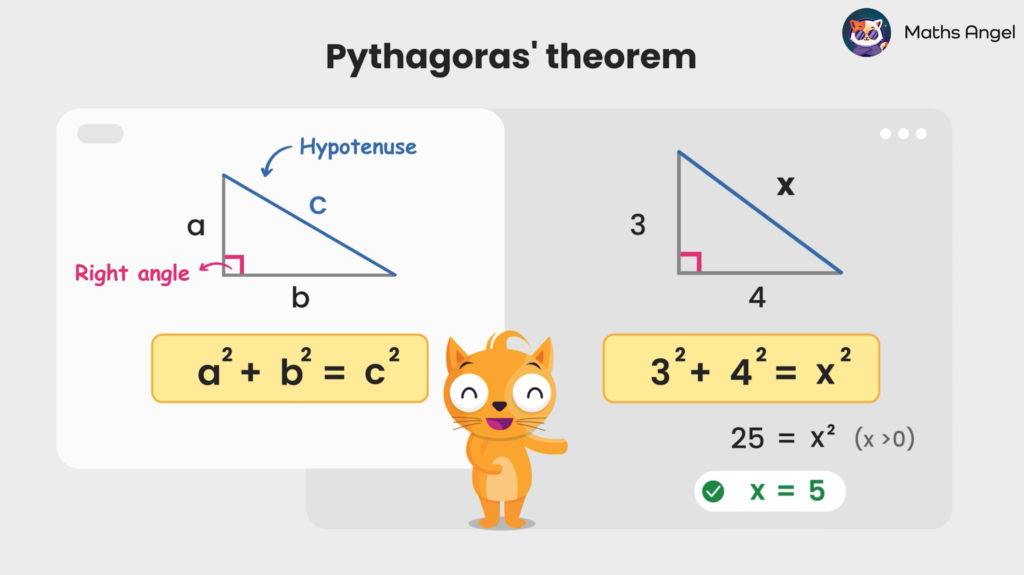
Open to access this content
Trigonometry: Sine, Cosine, Tangent
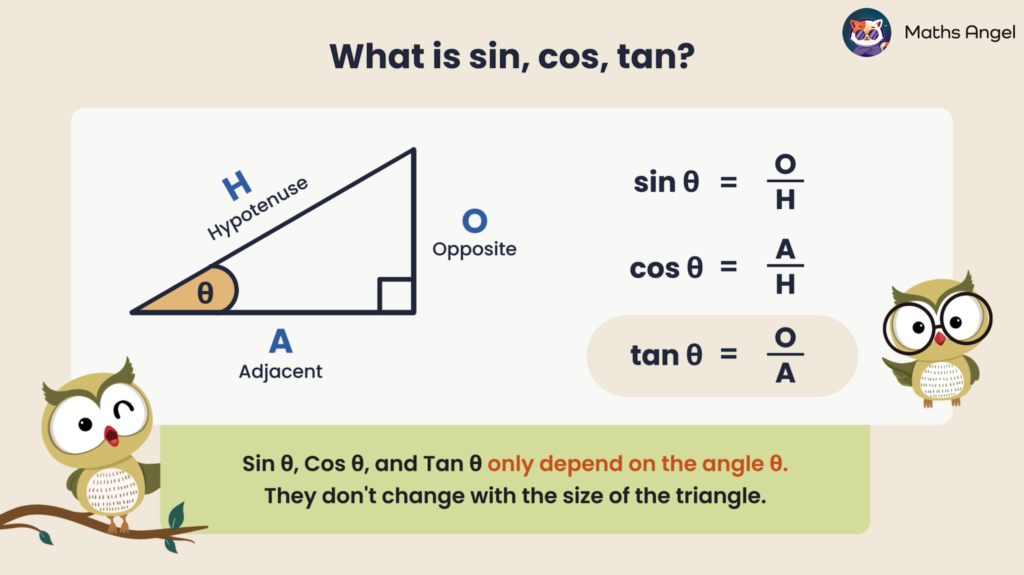
Open to access this content
Cosine Rule
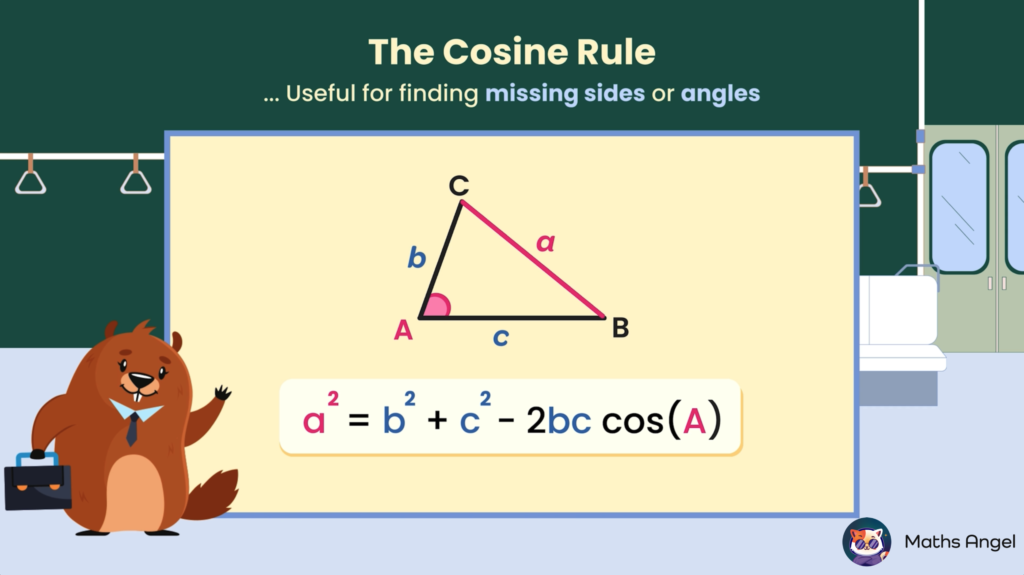
Open to access this content
Sine Rule
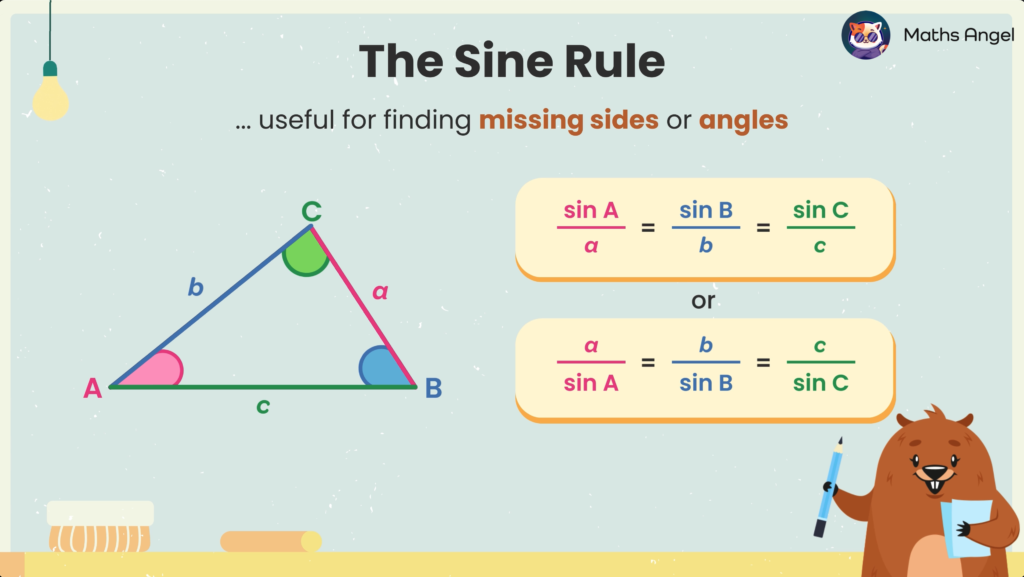
Open to access this content
