Pythagoras Theorem
Table Of Contents
🎬 Math Angel Video: Pythagoras Theorem Formula and Use
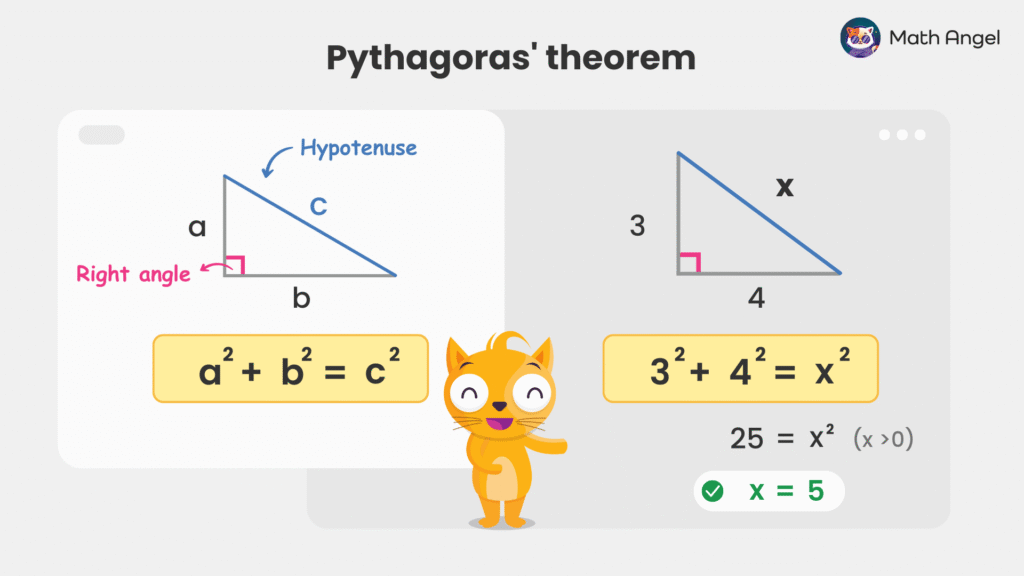
What is Pythagoras' Theorem?
⏩️
🛎️ Definition of Pythagoras’ Theorem:
Pythagoras’ Theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
🛎️ Formula of Pythagoras’ Theorem:
$$ a^2 + b^2 = c^2 $$
where:
- $a$ and $b$ are the two shorter sides (legs).
- $c$ is the hypotenuse (the longest side opposite the right angle).
🛎️ How to Use Pythagoras’ Theorem:
Given a right-angled triangle with two legs measuring 3 and 4, find the hypotenuse $x$.
- Step 1: Use Pythagoras’ Theorem: $$ 3^2 + 4^2 = x^2 $$
- Step 2: Simplifying the equations:
$$
\begin{aligned}
9 + 16 &= x^2 \\
x^2 &= 25
\end{aligned}
$$
- Step 3: Take the positive square root (since a length cannot be negative):
$$ x = \sqrt{25} = 5 $$
✅ Final Answer: Thus, the hypotenuse is 5.
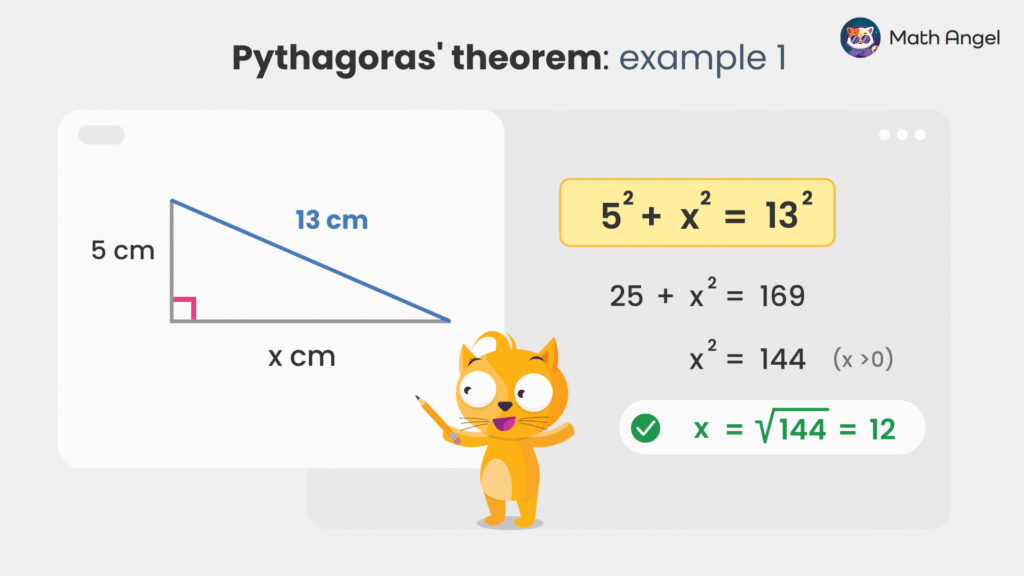
How to Use Pythagoras' Theorem to Find Side?
⏩️
You can use Pythagoras’ Theorem to find the missing side in a right-angled triangle.
🛎️ Example:
Given a right-angled triangle with one side of 5 and hypotenuse of 13. Find the other side $x$.
- Step 1: Use Pythagoras’ Theorem: $$ 5^2 + x^2 = 13^2 $$
- Step 2: Simplifying the equations:
$$
\begin{aligned}
25 + x^2 &= 169 \\
x^2 &= 144
\end{aligned}
$$
- Step 3: Take the positive square root (since a length cannot be negative):
$$ x = \sqrt{144} = 12 $$
✅ Final Answer: Thus, the hypotenuse is 5.
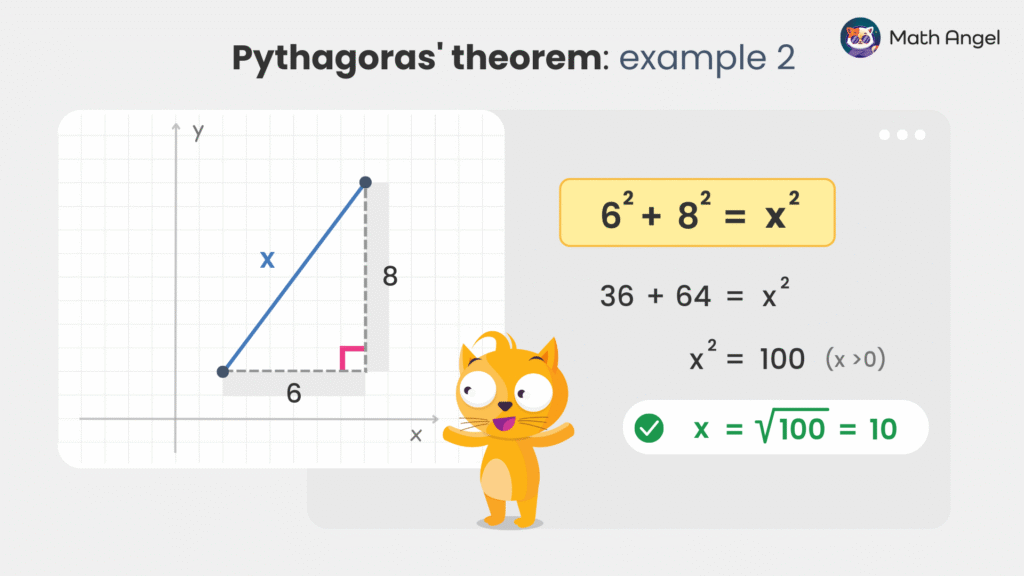
Using Pythagoras’ Theorem to Find Distance on a Grid
⏩️
We can use Pythagoras’ Theorem to find the straight-line distance between two points on a coordinate grid.
To do this:
- Plot the two points on the grid.
- Draw a horizontal line and a vertical line from one point to the other to form a right-angled triangle.
- The horizontal and vertical lines are the legs, and the diagonal line joining the points is the hypotenuse.
🛎️ Example:
Find the distance between the two points.
Horizontal distance = 6
Vertical distance = 8
- Step 1: Use Pythagoras’ Theorem: $$ 6^2 + 8^2 = x^2 $$
- Step 2: Simplifying the equations:
$$
\begin{aligned}
36 + 64 &= x^2 \\
x^2 &= 100
\end{aligned}
$$
- Step 3: Take the positive square root (since a length cannot be negative):
$$ x = \sqrt{100} = 10 $$
✅ Final Answer:The distance between the two points is 10.
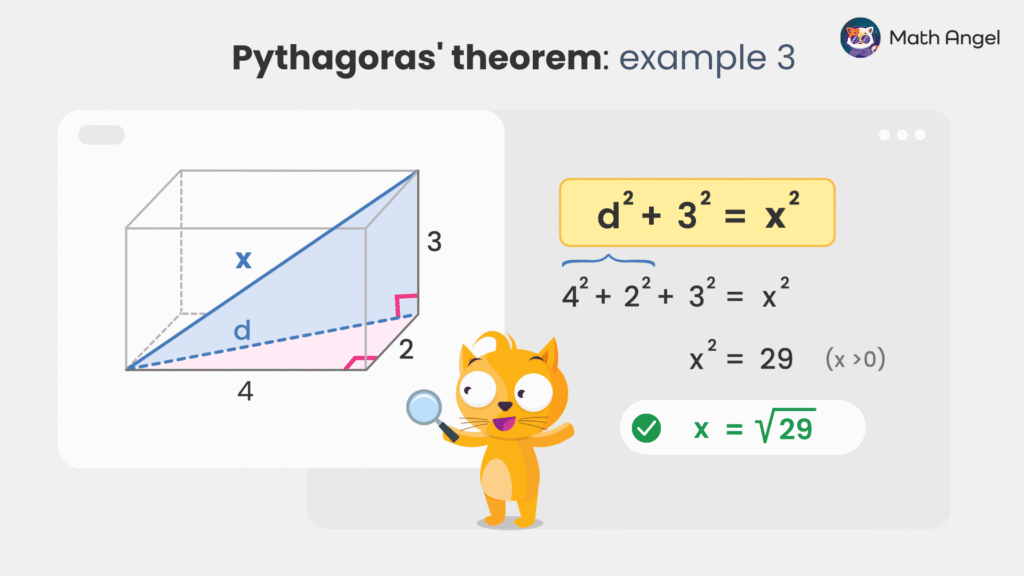
Applying Pythagoras' Theorem in 3D
⏩️
Pythagoras’ Theorem can also be used in three dimensions to find the space diagonal of a cuboid. The trick is to apply Pythagoras’ Theorem twice.
🛎️ Example:
Given a cuboid with side lengths 4, 2, and 3, find the space diagonal $x$:
- Step 1: First, find the diagonal of the base $d$ using Pythagoras’ Theorem:
\begin{aligned}
d^2 &= 4^2 + 2^2 \\[0.5em]
d^2 &= 16 + 4 \\[0.5em]
d^2 &= 20
\end{aligned}
- Step 2: Now, use Pythagoras’ Theorem again to find the full space diagonal $x$:
$$ d^2 + 3^2 = x^2 $$
$$ 20 + 9 = x^2 $$
$$ x = \sqrt{29} $$
Thus, the space diagonal of the cuboid is $\sqrt{29}$.
🍪 Quiz: Pythagoras Theorem and Right Angled Triangles
Membership Required
You must be a member of Math Angel Plus or Math Angel Unlimited to view this content.
🎩 Stuck on Pythagoras Problems? Try AI Math Solver
Need math help? Chat with our AI Math Solver at the bottom right — available 24/7 for instant answers.

