Converting Quadratics: Standard Form and Vertex Form
Table Of Contents
🎬 Math Angel Video: Converting Quadratics Step by Step
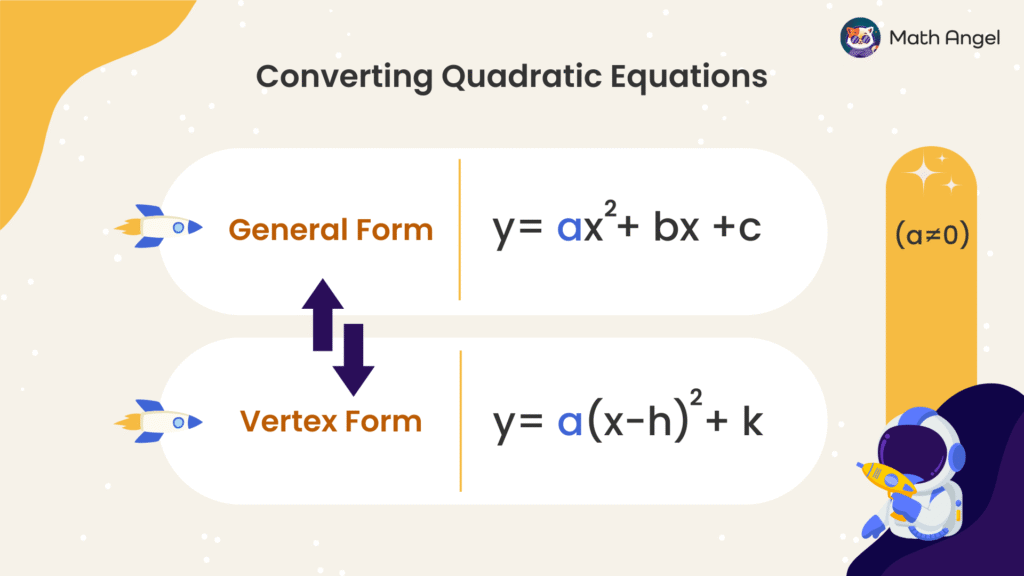
What are the Standard Form and Vertex Form?
⏩️
Quadratic equations can be written in two different forms:
- Standard Form (also known as the General Form):
$$
y = ax^2 + bx + c
$$
- Vertex Form:
$$
y = a(x\ – \ h)^2 + k
$$
In both forms, $ a \ne 0 $.
They’re two ways of expressing the same quadratic relationship:
Use the standard form $ y = ax^2 + bx + c $ when you’re solving or simplifying algebraically.
Use the vertex form $ y = a(x\ – \ h)^2 + k $ when you want to find the vertex easily.
So, you can switch between the two forms depending on what the question is asking.
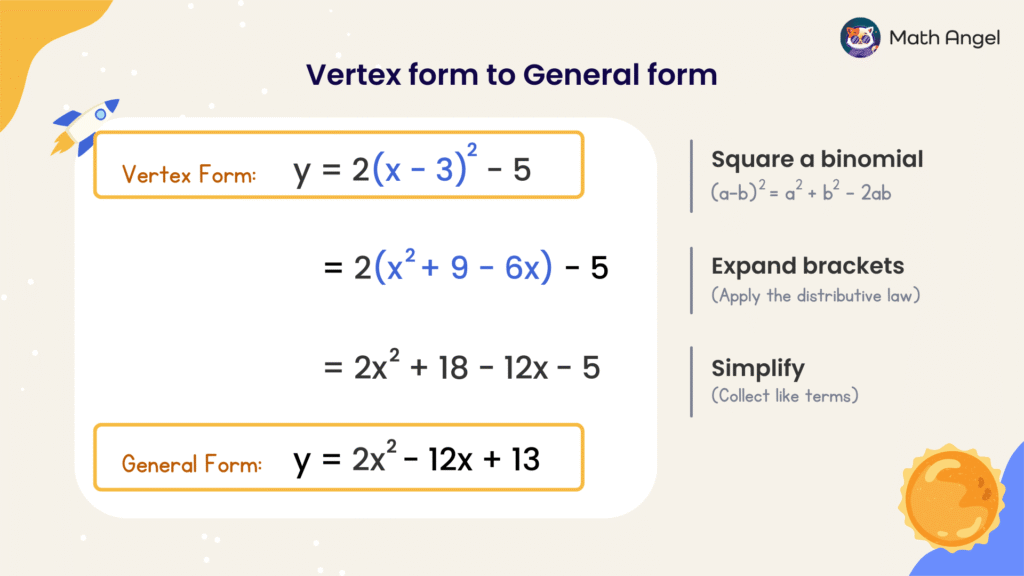
How to convert Vertex Form to Standard Form?
⏩️
To convert from vertex form to standard form, follow these steps:
$$
y = 2(x\ – \ 3)^2\ – \ 5
$$
- Step 1: Square the Binomial
Applying the formula:
$$
(a\ – \ b)^2 = a^2\ – \ 2ab + b^2
$$
$$
(x\ – \ 3)^2 = x^2\ – \ 6x + 9
$$
- Step 2: Expand the brackets
Multiply each term inside the bracket by 2:
$$
\begin{aligned}
y &= 2(x^2\ – \ 6x + 9) \ – \ 5 \\[0.8em]
&= 2x^2\ – \ 12x + 18 \ – \ 5 \\[0.8em]
\end{aligned}
$$
Step 3: Simplify
Combine like terms: + 18 – 5 becomes + 13
So the standard form is:
$$
y = 2x^2 \ – \ 12x + 13
$$
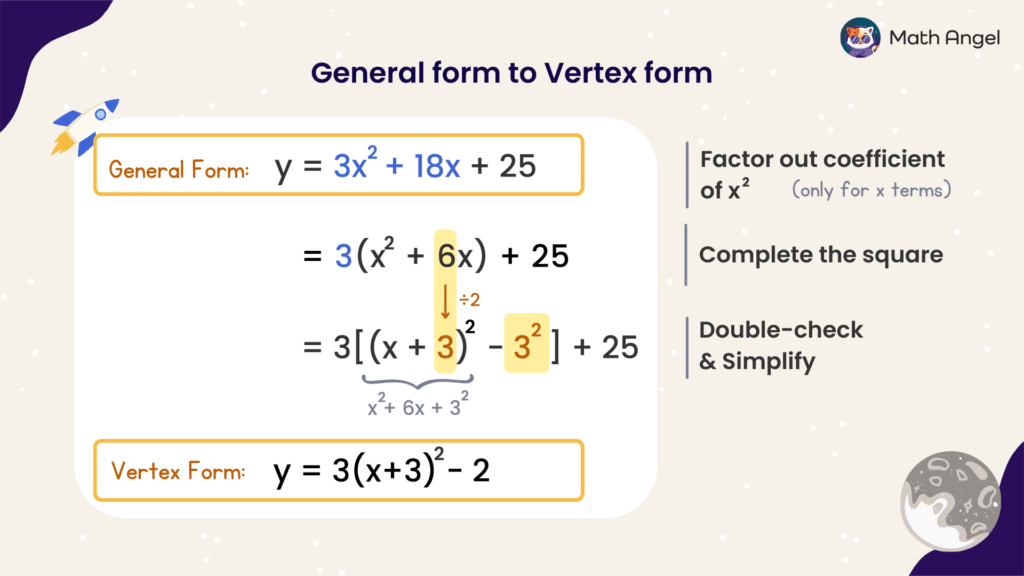
How to Write a Quadratic Equation in Vertex Form?
⏩️
To convert from standard form to vertex form, follow these steps:
$$
y = 3x^2 + 18x + 25
$$
- Step 1: Factor out the coefficient of $x^2$
The coefficient of $x^2$ is 3, so we factor out 3 from the first two terms: the $x^2$ and $x$ terms.
$$
y = 3(x^2 + 6x) + 25
$$
- Step 2: Complete the square
- Take half of 6 (which is 3), square it (which is 9), then add and subtract it inside the bracket:
$$
y = 3(x^2 + 6x + 9 \ – \ 9) + 25
$$
- Group the first 3 terms to form a perfect square:
$$
y = 3\left[(x^2 + 6x + 9)\ – \ 9\right] + 25
$$
- Now write the trinomial as a square:
$$
y = 3\left[(x + 3)^2\ – \ 9\right] + 25
$$
- Step 3: Simplify
- Distribute the 3 (and don’t forget the constant!)
$$
y= 3(x + 3)^2\ – \ 27 + 25
$$
- Combine like terms: – 27 +25 becomes – 2
So the vertex form is:
- Combine like terms: – 27 +25 becomes – 2
$$
y = 3(x + 3)^2 \ – \ 2
$$
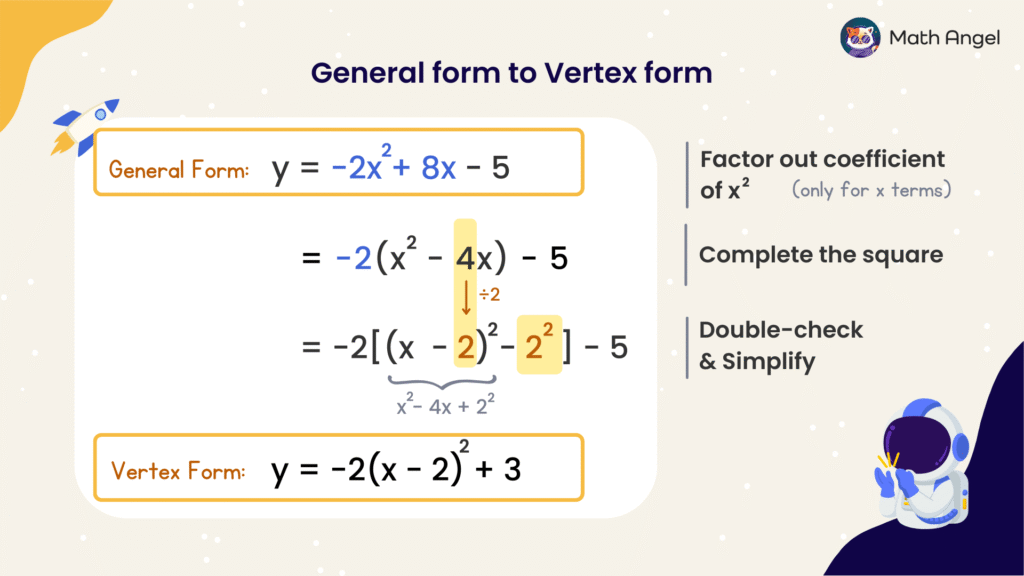
Converting General Form to Vertex Form (Example)
⏩️
To convert from general form to vertex form, follow these steps:
$$
y = -2x^2 + 8x \ – \ 5
$$
- Step 1: Factor out the coefficient of $x^2$
The coefficient of $x^2$ is $-2$, so we factor out $-2$ from the first two terms: the $x^2$ and $x$ terms.
$$
y = -2(x^2\ – \ 4x)\ – \ 5
$$
- Step 2: Complete the square
- Take half of $-4$ (which is $-2$), square it (which is $4$), then add and subtract it inside the bracket:
$$
y = -2(x^2\ – \ 4x + 4\ – \ 4)\ – \ 5
$$
-
- Group the first 3 terms to form a perfect square:
$$
y = -2\left[(x^2\ – \ 4x + 4) \ – \ 4\right]\ – \ 5
$$
-
- Now write the trinomial as a square:
$$
y = -2\left[(x\ – \ 2)^2\ – \ 4\right]\ – \ 5
$$
- Step 3: Simplify
Distribute the $-2$ and simplify:
$$
y = -2(x\ – \ 2)^2 + 8 \ – \ 5
$$
Combine like terms: $+8 – 5$ becomes $+3$
So the vertex form is:
$$
y = -2(x\ – \ 2)^2 + 3
$$
🍪 Quiz: Practice Converting Quadratic Equations Between General and Vertex Form
Membership Required
You must be a member of Math Angel Plus or Math Angel Unlimited to view this content.
🎩 Stuck on Quadratic Equations? Try AI Math Solver
Need math help? Chat with our AI Math Solver at the bottom right — available 24/7 for instant answers.

