Long Division
Table Of Contents
🎬 Math Angel Video: Long Division Step by Step
What is Long Division?
⏩️
Long division is a step-by-step method for dividing large numbers. It helps you break down a big division problem into smaller, easier steps.
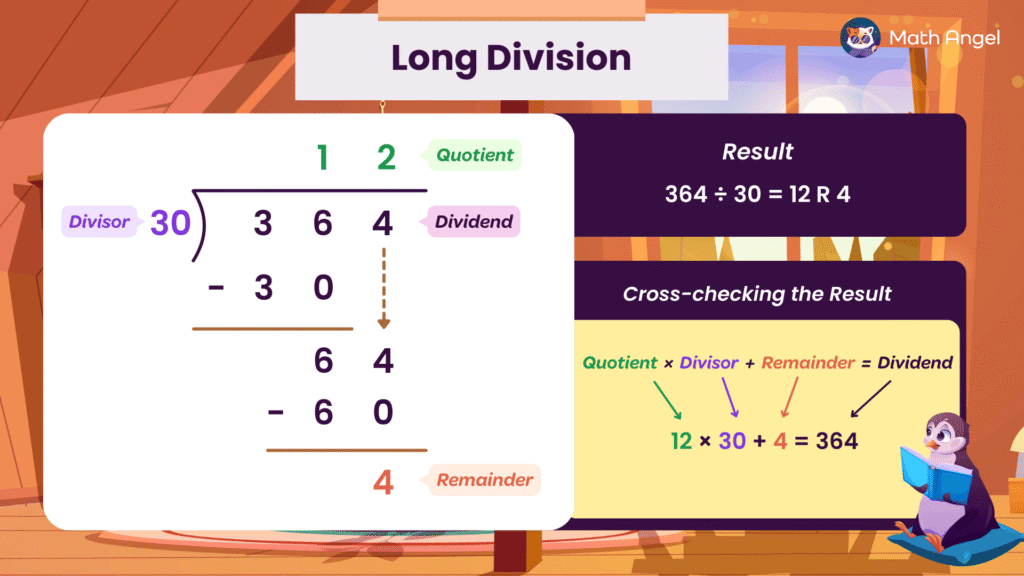
🛎 Let’s use long division to divide 364 by 30
- Set it up:
- 364 is the dividend (the number being divided).
- 30 is the divisor (the number you’re dividing by).
- Divide the first digits:
- 30 goes into 36 once.
- Write 1 above the 6 in the quotient area.
- Multiply: 1 × 30 = 30
- Subtract: 36 − 30 = 6
- Bring down the next digit (4):
- Now you have 64.
- Now you have 64.
- Divide again:
- 30 goes into 64 two times.
- Write 2 in the quotient
- Multiply: 2 × 30 = 60
- Subtract: 64 − 60 = 4
- Result:
- As there are no more digits to bring down, so 12 is the quotient, and 4 is the remainder.
- So: 364 ÷ 30 = 12 R 4
🛎 How To Check Your Long Division Answer:
To check your long-division answer, use this formula:
$$ \text{Quotient} \times \text{Divisor} + \text{Remainder} = \text{Dividend} $$
For example, you solved:
$$ 364 \div 30 = 12\ \text{R}\ 4$$
Let’s identify each part:
- Dividend = 364 → the number being divided
- Divisor = 30 → the number you’re dividing by
- Quotient = 12 → how many whole times 30 fits into 364
- Remainder = 4 → what’s left over
Substitute the numbers:
$$ 12 \times 30 + 4 = 360 + 4 = 364$$
It matches the original number (364), so the division is correct! ✅
How to Solve 1615 ÷ 7 Using Long Division
⏩️
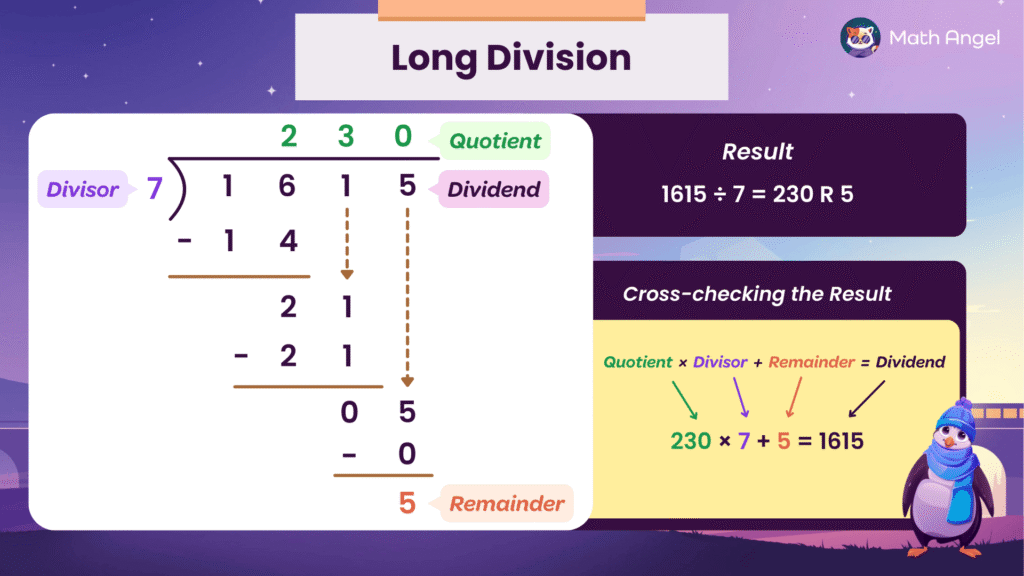
🛎 Let’s use long division to divide 1615 by 7
- Set it up:
- 1615 is the dividend (the number being divided).
- 7 is the divisor (the number you’re dividing by).
- Divide the first digits:
- 7 goes into 16 two times.
- Write 2 above the 6 in the quotient area.
- Multiply: 2 × 7 = 14
- Subtract: 16 − 14 = 2
- Bring down the next digit (1):
- Now you have 21
- 7 goes into 21 three times.
- Write 3 in the quotient
- Multiply: 3 × 7 = 21
- Subtract: 21 − 21 = 0
- Bring down the last digit (5):
- Now you have 5
- 7 goes into 5 zero times.
- Write 0 in the quotient
- Subtract: 5 − 0 = 5
Result:
- There are no more digits to bring down, so the quotient is 230, and the remainder is 5.
- So: 1615 ÷ 7 = 230 R 5
🛎 How To Check Your Long Division Answer:
To double-check that your calculation is correct, use this formula:
$$ \text{Quotient} \times \text{Divisor} + \text{Remainder} = \text{Dividend} $$
$$ 230 \times 7 + 5 = 1610 + 5 = 1615$$
It matches the original number (1615), so the division is correct! ✅
🍪 Quiz (6 Questions): Test Your Skills with Long Division
Membership Required
You must be a member of Math Angel Plus or Math Angel Unlimited to view this content.
🎩 Stuck on Long Division? Try Our AI Math Solver
Need math help? Chat with our AI Math Solver at the bottom right — available 24/7 for instant answers.

