{results_count} Math videos for {phrase}
Displaying {results_count} results of {results_count_total}
Thales’ Theorem
Table Of Contents
🎬 Math Angel Video: Thales' Theorem Definition and Application
What is Thales' Theorem?
⏩️
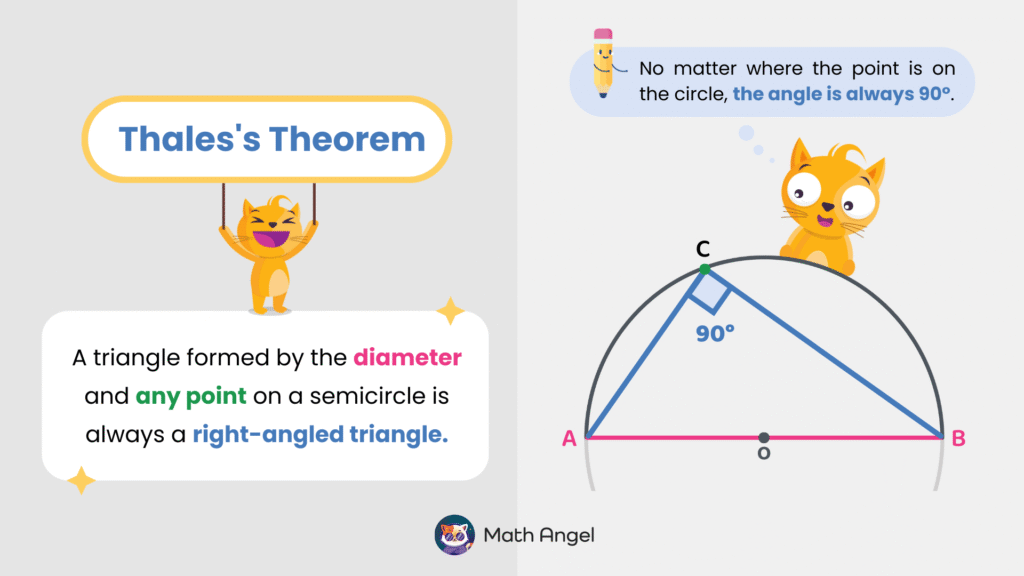
Thales’s theorem states that if a triangle is formed using the diameter of a circle and any point on the semicircle, it will always be a right-angled triangle.
In the diagram, AB is the diameter of the circle, and C is a point on the semicircle. No matter where C is, the angle at C is always 90°.
How to Apply Thales' Theorem?
⏩️
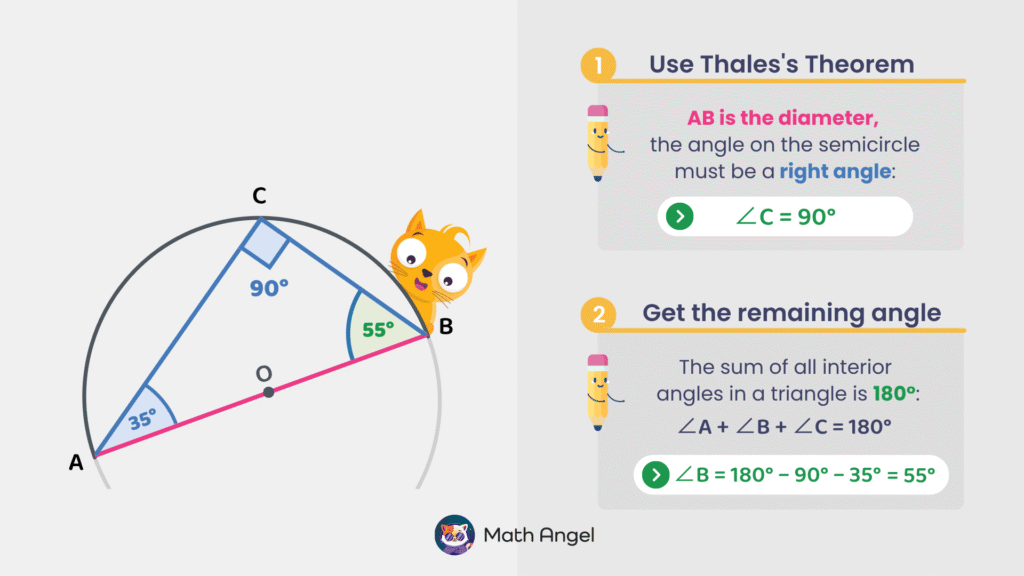
- Step 1: Use Thales’s Theorem
Since $AB$ is the diameter, and vertex $C$ is a point on the semicircle. Thus,
$$ \angle C = 90^\circ $$
- Step 2: Find the Remaining Angle
The sum of all angles in a triangle is:
$$ \angle A + \angle B + \angle C = 180^\circ $$
Since we know $ \angle C = 90^\circ $ and $ \angle A = 35^\circ $, we can find $ \angle B $:
$$ \angle B = 180^\circ – 90^\circ – 35^\circ = 55^\circ $$
Finding Angles Using Thales' Theorem (Practice)
⏩️
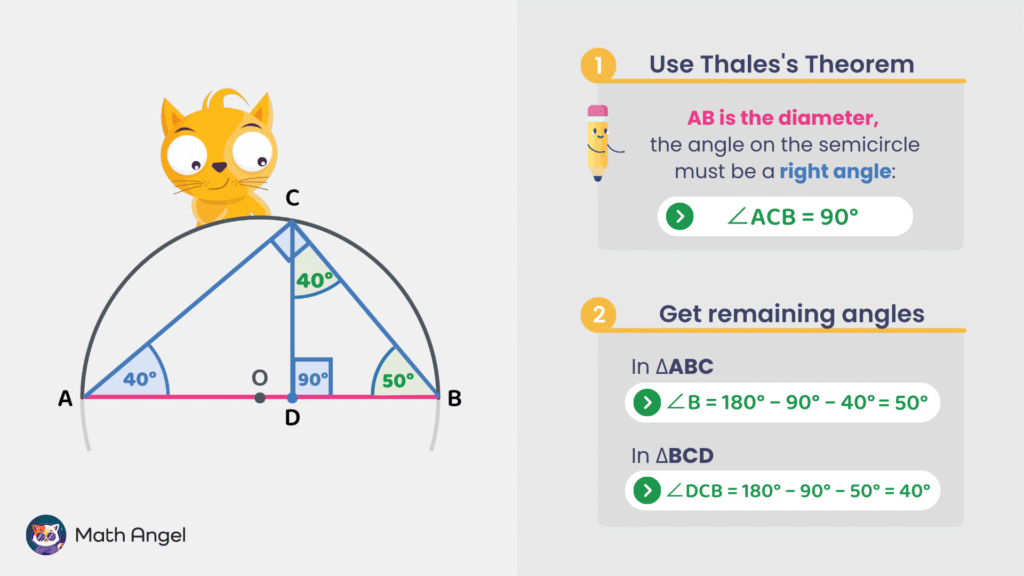
- Step 1: Use Thales’s Theorem
Since $AB$ is a diameter and $C$ lies on the semicircle, the angle at $C$ in $\triangle ABC$ is a right angle:
$$ \angle ACB = 90^\circ $$ - Step 2: Find the remaining angle in $\triangle ABC$
Angles in a triangle sum to $180^\circ$:
$$ \angle A + \angle B + \angle C = 180^\circ $$
Given $\angle A = 40^\circ$ and $\angle C = 90^\circ$,
$$ \angle B = 180^\circ – 90^\circ – 40^\circ = 50^\circ $$ - Step 3: Use $\triangle BCD$ to find $\angle DCB$
$\angle CDB = 90^\circ$, and $\angle B = 50^\circ$,
$$ \angle DCB = 180^\circ – 90^\circ – 50^\circ = 40^\circ $$
❇️ Exam Tip: Spot the diameter first, it instantly tells you where the right angle is.
🍪 Quiz: Test Your Skills with Thales' Theorem
0%
🎩 Curious About Circle Geometry? Try AI Math Solver
Need math help? Chat with our AI Math Solver at the bottom right — available 24/7 for instant answers.
5
1
vote
Article Rating
0 Comments
Newest
Oldest
Most Voted
Inline Feedbacks
View all comments

