Prime Numbers and Prime Factorization
Table Of Contents
What Are Prime Numbers?

⏩️
🛎️ Definition of Prime numbers:
Prime numbers are natural numbers that have exactly two different factors: 1 and the number itself.
- ✅ 2 is a prime number because it has only two factors: 1 and 2.
- ❌ 4 is not a prime number because it has three factors: 1, 2, and 4.
- ❌ 1 is not a prime number because it only has one factor: 1.
❇️ Exam tip: 2 is the smallest and only even prime number.
What are Common Prime Numbers?

⏩️
Prime numbers are often called the “building blocks” of mathematics because every whole number can be made by multiplying primes.
🛎️ Prime Numbers Below 20 Are:
$$2,\ 3,\ 5,\ 7,\ 11,\ 13,\ 17,\ 19$$
🛎️ Non-Prime Numbers Below 20 Are:
$$1,\ 4,\ 6,\ 8,\ 9,\ 10,\ 12,\ 14,\ 15,\ 16,\ 18 $$
❇️ Exam tip: Try to memorise the prime numbers:) They show up a lot in maths exams, especially in questions about factors and multiples.
How to Do Prime Factorization Step by Step
⏩️
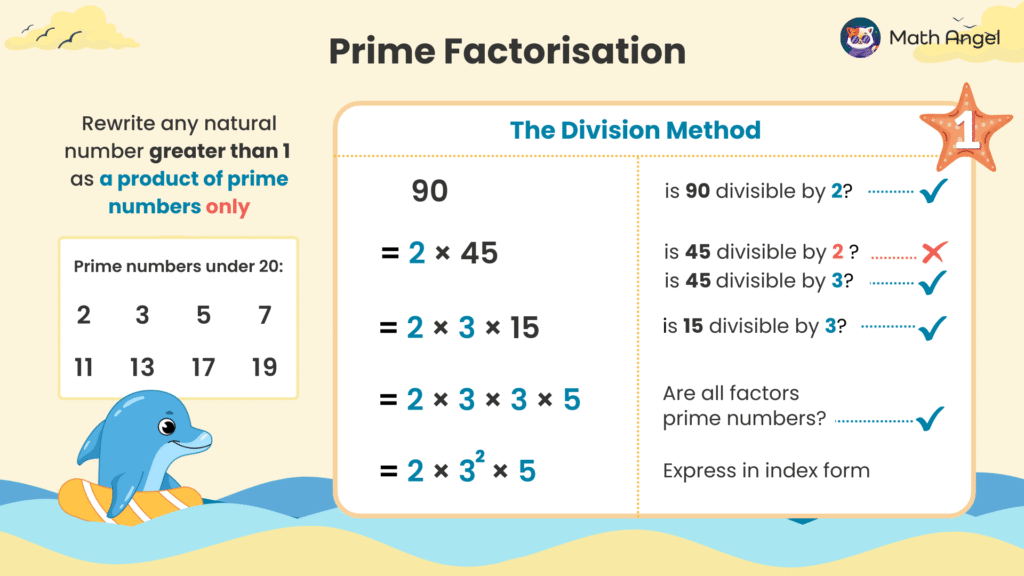
🛎️ What Does Prime Factorization Mean?
Prime factorization means writing a number as a product of prime numbers only.
One method is using division.
🛎️ Example of Prime Factorization:
Let’s factorise 90 step by step:
Start with the smallest prime number (2) that divides 90:
$$90 = 2 \times 45$$
Try dividing 45 by the next smallest prime (3):
$$ 90 = 2 \times 3 \times 15 $$
15 is not a prime number, so we keep dividing:
$$ 90 = 2 \times 3 \times 3 \times 5$$
- All the numbers are now prime. So the final answer in index form is:
$$ 90 = 2 \times 3^2 \times 5 $$
How to Use a Factor Tree for Prime Factorization
⏩️
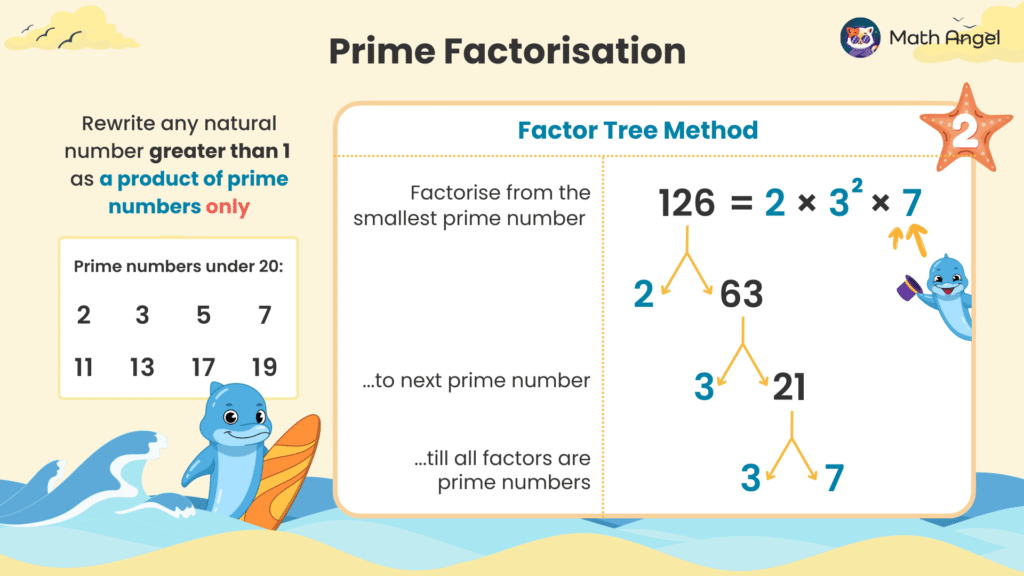
🛎️ What Is A Factor Tree?
A factor tree is a visual method to break a number down into its prime factors step by step.
🛎️ Example of Prime Factorisation:
Let’s start with 126.
Start with the smallest prime number (2):
$$126 = 2 \times 63$$Continue factoring the next number (3):
$$63 = 3 \times 21$$21 is not a prime number, so we continue dividing:
$$21 = 3 \times 7$$Now, all factors are prime numbers:
$$126 = 2 \times 3 \times 3 \times 7$$
- The Final answer in index form:
$$126 = 2 \times 3^2 \times 7$$
❇️ Exam tip: This method helps you see the breakdown clearly and is especially useful for math exams.
🍪 Quiz: Test Your Prime Factorization Skills
Membership Required
You must be a member of Math Angel Plus or Math Angel Unlimited to view this content.
🎩 Stuck on Prime Factorisation? Try AI Math Solver
Need math help? Chat with our AI Math Solver at the bottom right — available 24/7 for instant answers.

