How to Calculate the Mean, Median, Mode, and Range
Table Of Contents
🎬 Math Angel Video: Mean, Median, Mode, Range Explained
How to Find the Mean?
⏩️
🛎️ What is the Mean?
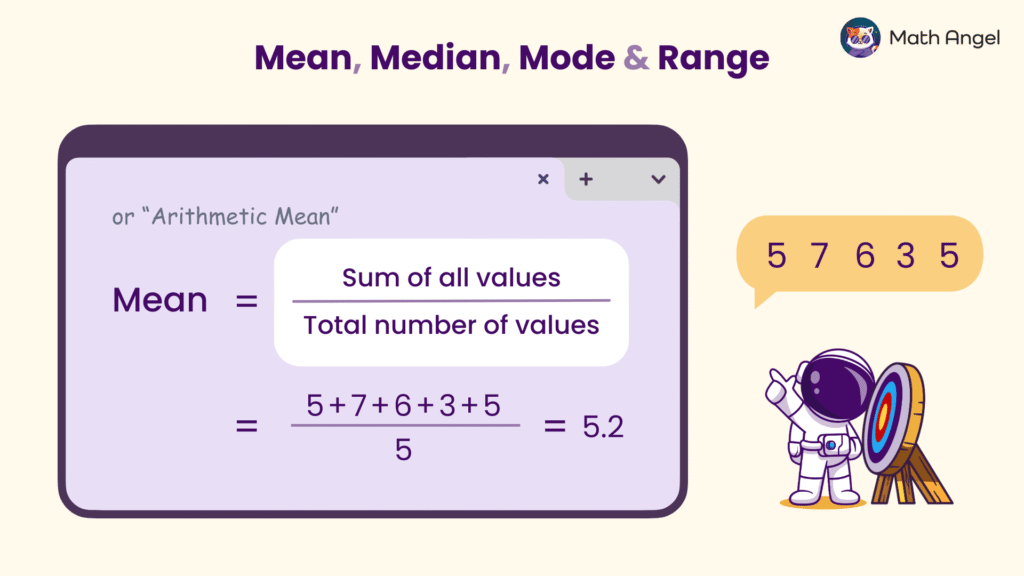
Mean, or Arithmetic Mean, tells you the average value of a set of numbers.
🛎️ How Do You Calculate the Mean?
You calculate the mean by dividing the sum of all values by the total number of values:
$$ \text{Mean} = \frac{ \text{Sum of all values}}{\text{Total number of values}} $$
🛎️ Example of Finding the Mean:
Imagine your scores in archery are: 5, 7, 6, 3, 5. To find your average score, you can calculate the mean:
- Step 1: Add up all the scores: $$5 + 7 + 6 + 3 + 5 = 26 $$
- Step 2: Divide by the total number of shots
$$ \text{Mean} = \frac{5 + 7 + 6 + 3 + 5}{5} = \frac{26}{5} = 5.2 $$
- This means, on average, your archery score is 5.2.
How to Find the Median?
⏩️
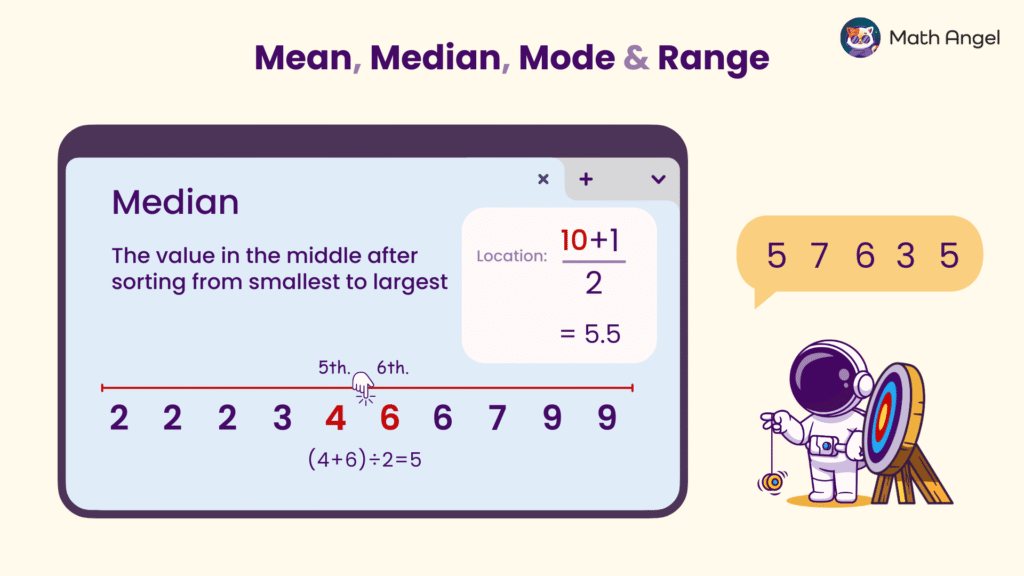
🛎️ What is the Median?
The median is the value in the middle after sorting the numbers from smallest to largest.
🛎️ How Do You Calculate the Median?
- If the number of values is odd, the middle number is the median.
- Example: Scores after sorting = 3, 5, 5, 6, 7
- Here, 5 is in the middle, so Median = 5
- If the number of values is even, take the average of the two middle numbers.
- Example: Scores after sorting = 3, 5, 5, 6, 7, 7
- The middle numbers are 5 and 6. To find their average, add them and divide by 2:
$$ \text{Median} = \frac{5 + 6}{2} = \frac{11}{2} = 5.5 $$
What is the Mode?
⏩️
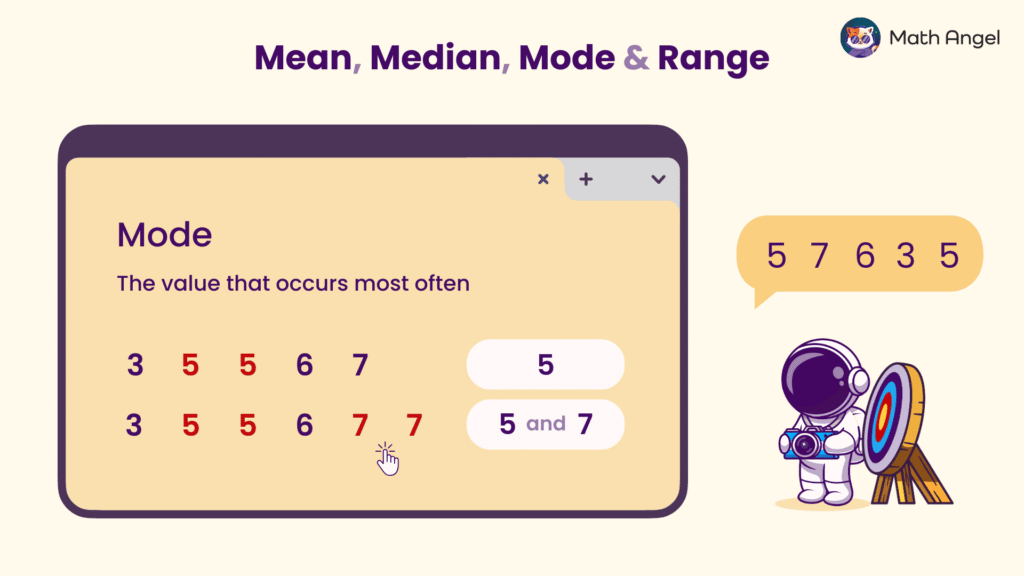
🛎️ What is the Mode?
The mode is the value that appears most often in a set of numbers.
- Example 1: Scores = 3, 5, 5, 6, 7
Here, 5 appears twice, while other numbers only appear once. So, Mode = 5 - Example 2: Scores = 3, 5, 5, 6, 7, 7
Here, 5 and 7 both appear twice, more than the others. So, Mode = 5 and 7
❇️ Exam tip: A data set can have:
- one mode (if one number appears most often),
- more than one mode (if multiple numbers appear with the same highest frequency),
- no mode at all (if no number repeats).
What is the Range?
⏩️
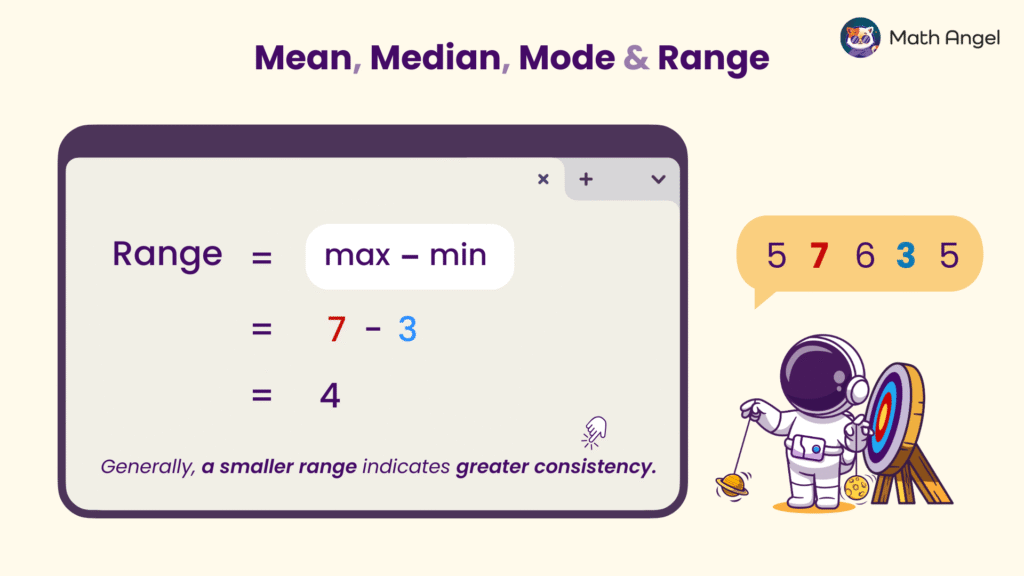
🛎️ What is the Range?
The range shows the spread of a data set. You find the range by subtracting the smallest value from the largest value:
$$ \text{Range} = \text{max value} \; – \; \text{min value} $$
- For example: 5, 7, 6, 3, 5
- Max value = 7
- Min value = 3
- So the Range is 7−3=4
🛎️ What the Range Tells You:
- A small range means the numbers are close together → The data is more consistent, and the results are steadier or more reliable.
- A large range means the numbers are spread out → The data is less consistent and shows more variation.
🍪 Quiz: Test Your Skills on Mean and Median
🎩 Stuck on Mean or Median? Try AI Math Solver
Need math help? Chat with our AI Math Solver at the bottom right — available 24/7 for instant answers.

