Elimination Method for Solving Simultaneous Equations
Table Of Contents
🎬 Math Angel Video: Elimination Method Step-by-Step
What is Elimination Method?
⏩️
The Elimination Method is a technique for solving systems of equations by adding or subtracting equations to eliminate one variable.
How to Do Elimination Method?
⏩️
🛎️ Example:
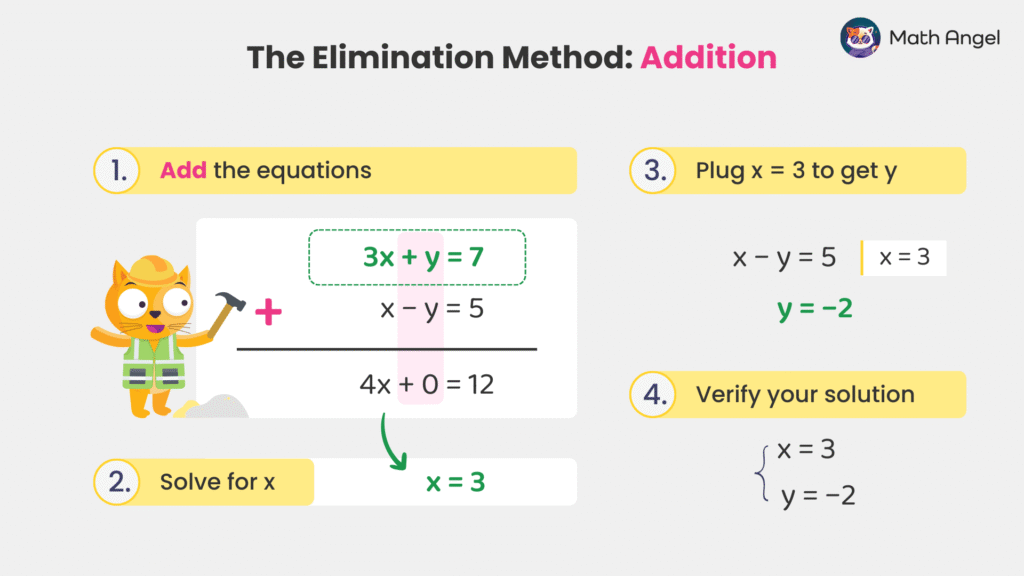
Given the simultaneous equations:
$$
\begin{cases}
3x + y = 7 \\
x\, -\, y = 5
\end{cases}
$$
- Step 1: Add the equations to eliminate $y$:
$$
\begin{aligned}
(3x + y) + (x\, -\,y) &= 7 + 5 \\[1em]
4x &= 12
\end{aligned}
$$
- Step 2: Solve for $x$: $$ x = 3 $$
- Step 3: Substitute $ x = 3 $ into any equation to find $y$, preferably the simpler one:
$$x\, -\, y = 5 \Rightarrow y = x\, -\, 5 = -2 $$
- Step 4: Verify the solution:
$$ \{ x = 3, \quad y = -2 \} $$
Solving Simultaneous Equations (Addition Example)
⏩️
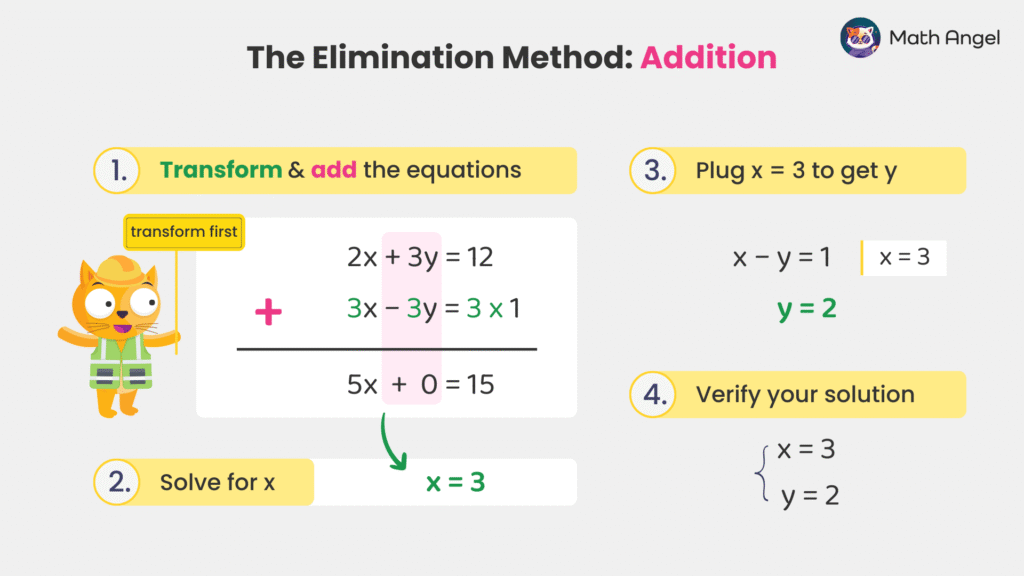
To eliminate a variable, we may need to adjust the equations by multiplying one or both of them so that adding or subtracting eliminates a variable.
🛎️ Example:
$$
\begin{cases}
2x + 3y = 12 \\
x\, -\, y = 1
\end{cases}
$$
- Step 1: Multiply the second equation by 3:
$$
\begin{cases}
2x + 3y = 12 \\
3x\, -\, 3y = 3
\end{cases}
$$
- Step 2: Add the equations to eliminate $y$:
$$
\begin{aligned}
(2x + 3y) + (3x\, -\, 3y) &= 12 + 3 \\[1em]
5x &=15
\end{aligned}
$$
- Step 3: Solve for $x$: $$ x = 3 $$
- Step 4: Substitute $ x = 3 $ into any equation to find $y$, preferably the simpler one:
$$ x\, -\, y = 1 \Rightarrow y = x\, -\,1=2 $$
- Step 5: Verify the solution:
$$ \{ x = 3, \quad y = 2 \} $$
Solving Simultaneous Equations (Subtraction Example)
⏩️
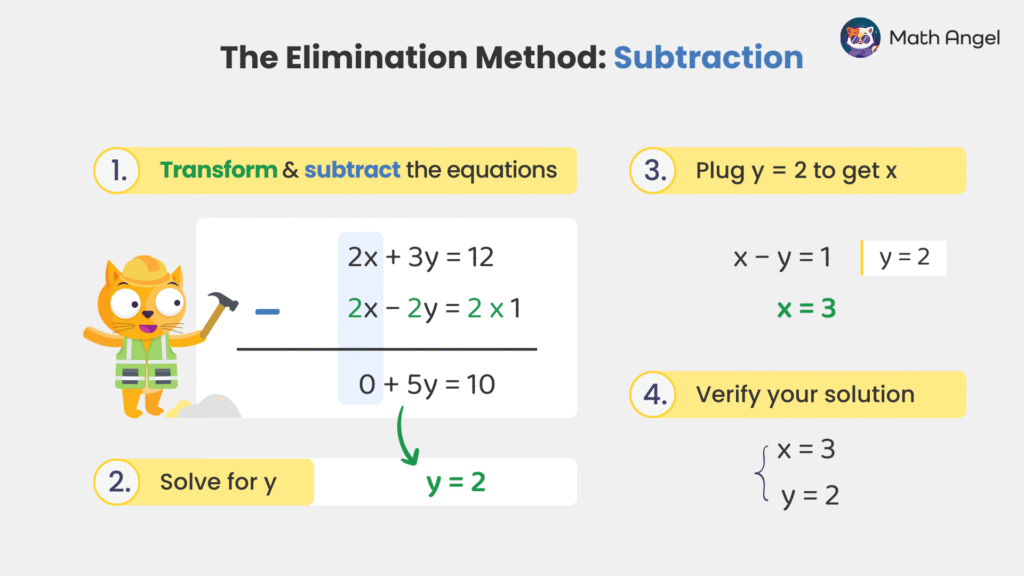
Instead of adding the equations, you can also subtract the equations to eliminate a variable.
🛎️ Example:
$$
\begin{cases}
2x + 3y = 12 \\
x\, -\, y = 1
\end{cases}
$$
- Step 1: Multiply the second equation by 2:
$$
\begin{cases}
2x + 3y = 12 \\
2x\, -\, 2y = 2
\end{cases}
$$
- Step 2: Subtract the equations:
$$
\begin{aligned}
(2x + 3y)\, -\, (2x\, -\, 2y) &= 12\, -\, 2 \\[1em]
5y &= 10
\end{aligned}
$$
- Step 3: Solve for $y$:
$$ y = 2 $$
- Step 4: Substitute $ y = 2 $ into any equation to find $x$, preferably the simpler one:
$$x\, -\, y = 1 \Rightarrow x = 2 + 1 = 3 $$
- Step 5: Verify the solution:
$$ \{ x = 3, \quad y = 2 \} $$
The Elimination Method (Addition vs Subtraction)
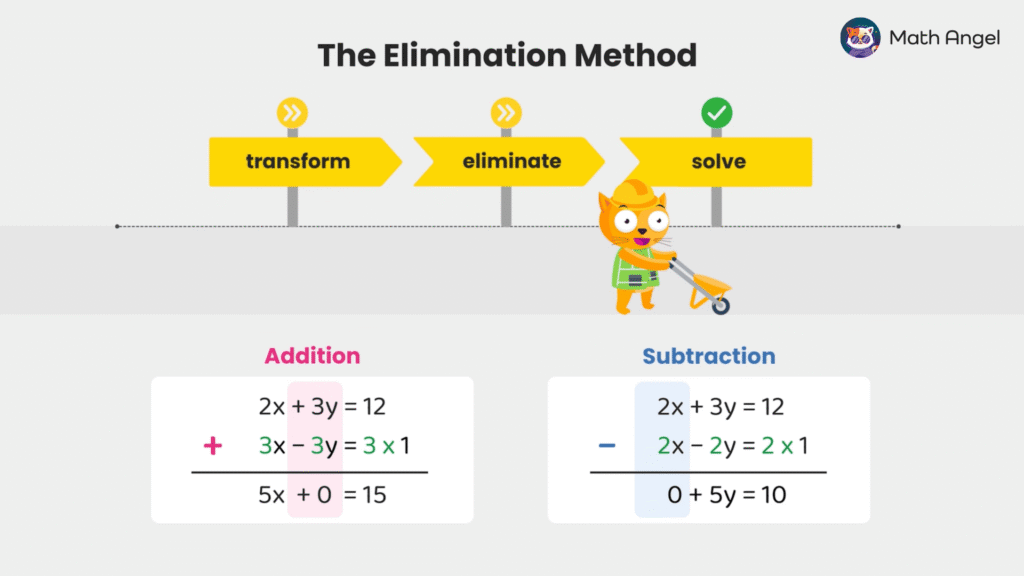
⏩️
Let’s learn when to add or subtract equations to eliminate a variable.
Look at the signs of the variable you want to eliminate:
If the signs are the same in both equations, subtract one equation from the other to eliminate that variable.
Example: to eliminate $x$$$
\begin{cases}
2x + 3y &= 12 \\
2x + 2y &= 10
\end{cases}
$$
Subtract → $y=2$If the signs are different, add the equations to eliminate that variable.
Example: to eliminate y$$$$
\begin{cases}
2x + 3y &= 12 \\
3x\, -\, 3y &= 3
\end{cases}
$$
Add → $5x=15$
❇️ Exam Tip: Remember same signs, subtract; different signs, add.
🍪 Quiz: Solve Simultaneous Equations with Elimination
Membership Required
You must be a member of Math Angel Plus or Math Angel Unlimited to view this content.
🎩 Stuck on Systems of Equations? Try AI Math Solver
Need math help? Chat with our AI Math Solver at the bottom right — available 24/7 for instant answers.

