Constructing Triangles
Table Of Contents
🎬 Math Angel Video: Constructing Triangles Step by Step
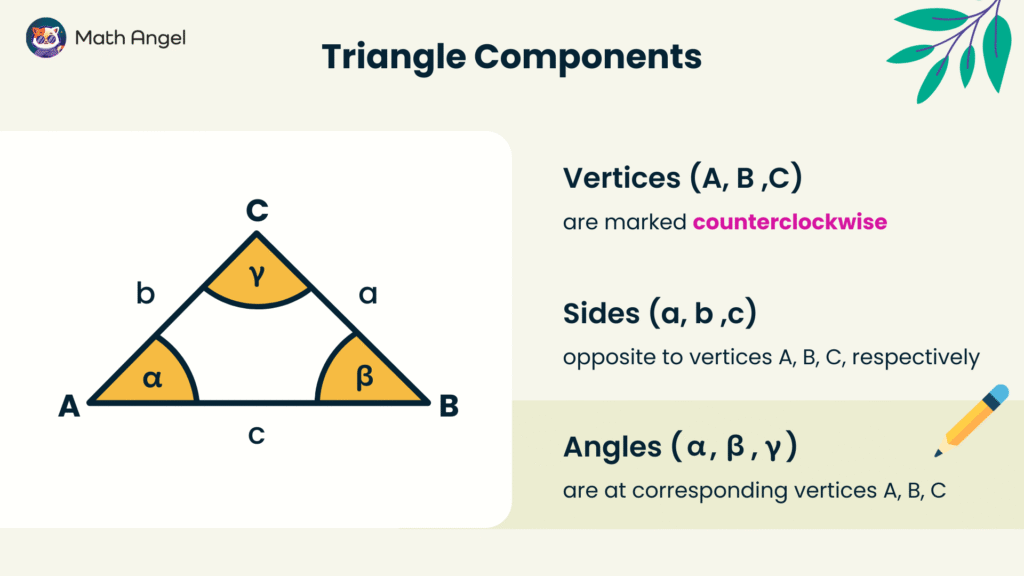
What are Components of a Triangle?
⏩️
🛎 What is a Triangle?
A triangle is a three-sided polygon consisting of three vertices, sides, and angles.
- Vertices (A, B, C): These are the corner points of the triangle.
- Sides (a, b, c): These are the edges of the triangle.
- Side a is opposite vertex A
- Side b is opposite vertex B
- Side c is opposite vertex C
- Angles (α, β, γ): These are the interior angles at each vertex.
- α is at vertex A
- β is at vertex B
- γ is at vertex C
Understanding these components is essential for constructing triangles accurately.
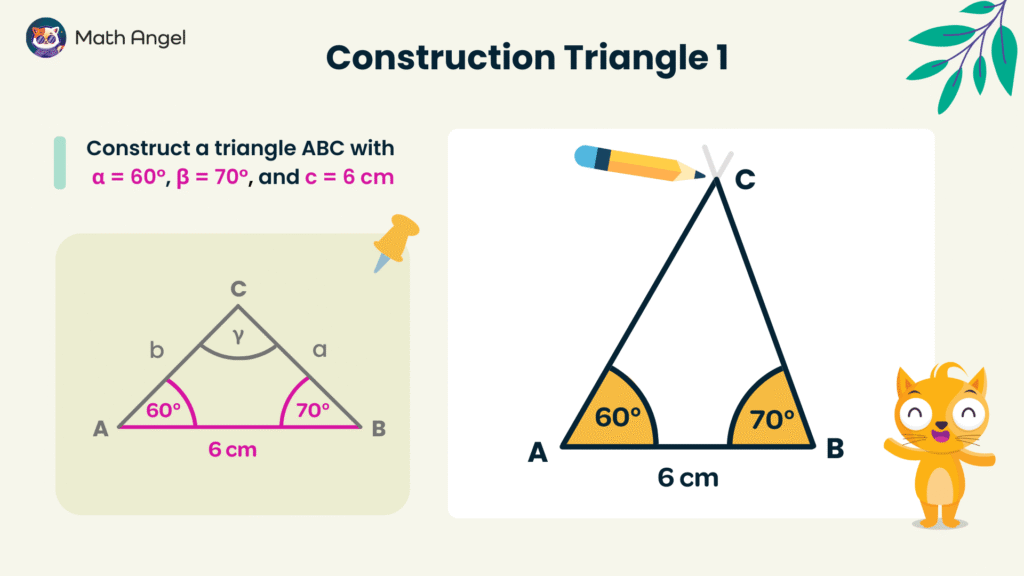
How to Construct a Triangle Using ASA?
⏩️
🛎 Constructing Triangles Using ASA
If you know two angles and the included side, you can construct a unique triangle based on the ASA (Angle-Side-Angle) rule.
- Draw the given side.
Start by drawing side AB = 6 cm as the base of the triangle. - Construct the first angle.
At point A, use a protractor to measure and draw angle 60°. - Construct the second angle.
At point B, use a protractor to draw angle 70°. - Complete the triangle.
Extend both angle lines until they meet at point C.
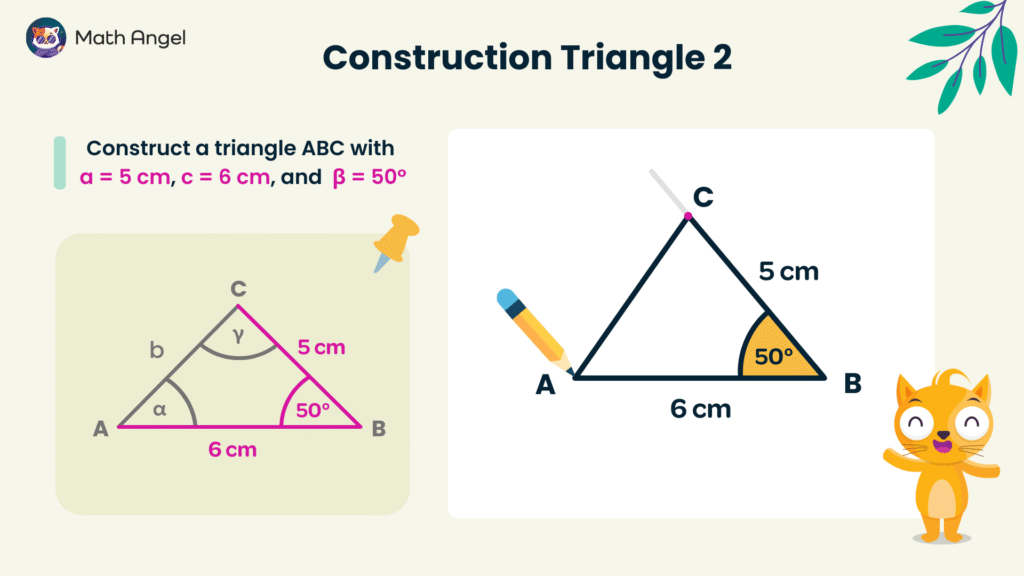
How to Construct a Triangle Using SAS?
⏩️
🛎 Constructing Triangles Using SAS
If you know two sides and the included angle, you can construct a unique triangle based on the SAS (Side-Angle-Side) rule.
- Draw the given side.
Start by drawing side AB = 6 cm as the base of the triangle. - Construct the given angle.
At point B, use a protractor to measure and draw angle 50°. - Draw the second side.
From point B, extend a line and mark point C such that BC = 5 cm. - Complete the triangle.
Connect point C to point A to form triangle ABC.
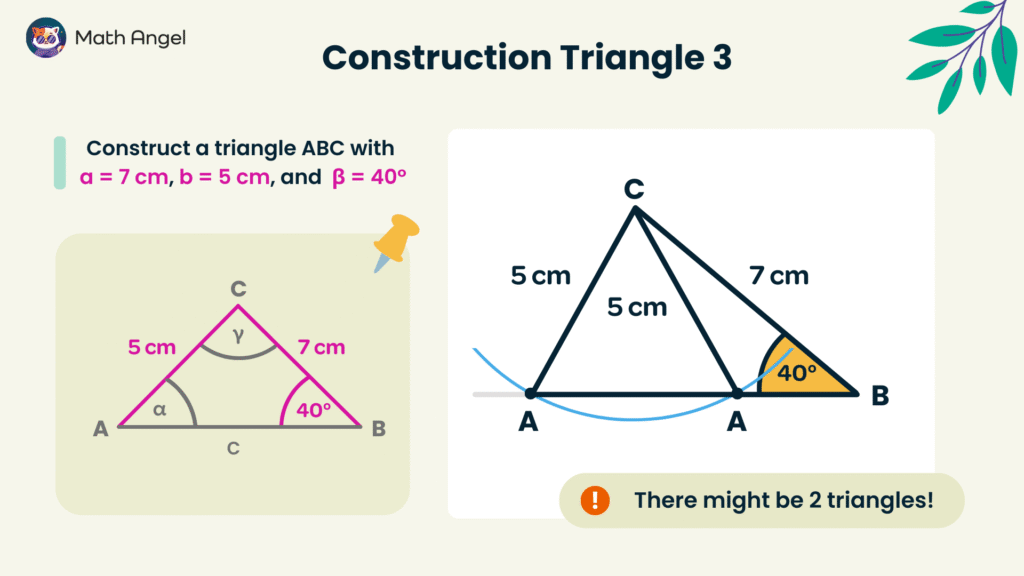
Constructing Triangles with SSA (Ambiguous Case)
⏩️
🛎 Common Pitfall with SSA
If you know two sides and a non-included angle, you may form two different triangles.
This is known as the Ambiguous Case in SSA (Side-Side-Angle) triangle construction.
- Draw the given side.
Start by drawing side AB = 7 cm as the base of the triangle. - Construct the given angle.
At point B, use a protractor to measure and draw angle 40°. - Use a compass for the second side.
Place the compass at point B and set it to 5 cm. Draw an arc that intersects the extended line from angle B. - Identify possible triangles.
The arc may intersect the line at two points, creating two possible triangles.
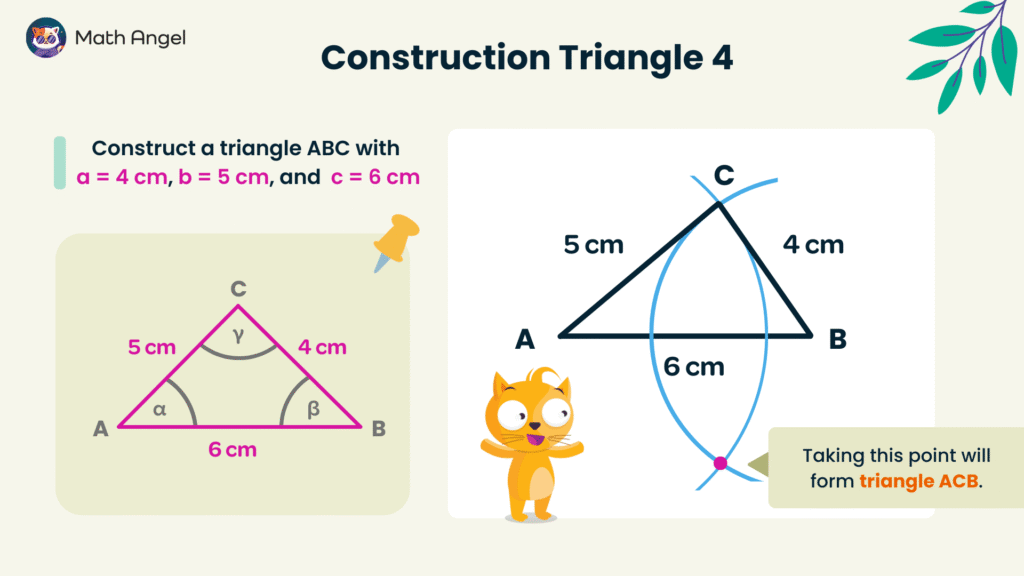
How to Construct a Triangle with SSS?
⏩️
🛎 Constructing Triangles Using SSS
If you know all three sides of a triangle, you can construct a unique triangle using the SSS (Side-Side-Side) rule.
- Draw the base.
Start by drawing side AB = 6 cm as the base of the triangle. - Use a compass for the other two sides.
- Place the compass at point A and set it to 5 cm. Draw an arc.
- Place the compass at point B and set it to 4 cm. Draw another arc.
- Find the intersection.
The two arcs will intersect at a point. Label this point as C. - Complete the triangle.
Connect points A to C and B to C to form triangle ABC.
🍪 Quiz: Test Your Skills on Triangle Construction
🎩 Stuck on Triangle Problems? Try AI Math Solver
Need math help? Chat with our AI Math Solver at the bottom right — available 24/7 for instant answers.

